Reaper Write-Up
Scenario Overview
For this Hack the Box challenge, we are given the Sherlock Scenario:
Our SIEM alerted us to a suspicious logon event that needs to be looked at immediately. The alert details were that the IP Address and the Source Workstation name were a mismatch. You are provided with a network capture and event logs from the time surrounding the incident. Correlate the given evidence and report back to your SOC Manager.
The “Reaper” scenario involves a suspicious logon event detected by our Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system. The alert was triggered due to a mismatch between the IP address and the source workstation name. This write-up details the steps taken to analyze the event, correlate the evidence, and identify the nature of the attack.
SIEM Alert Details
- Incident: Suspicious logon event
- Trigger: Mismatch between IP address and source workstation name
- Objective: Investigate the event, identify the attacker, and report findings to the SOC Manager.
- Difficulty: Very easy
Steps Taken
We worked with files located in Reaper.zip. After unzipping the file, we found the following:

What is the IP Address for Forela-Wkstn001?
We found the IP address for Forela-Wkstn001 by opening the
ntlrelay.pcapngfile in Wireshark. We filtered the data using the NBNS (NetBIOS Name Service) protocol, which is used for name resolution on older networks. This helped us see the correct IP address for this workstation:Answer:
172.17.79.129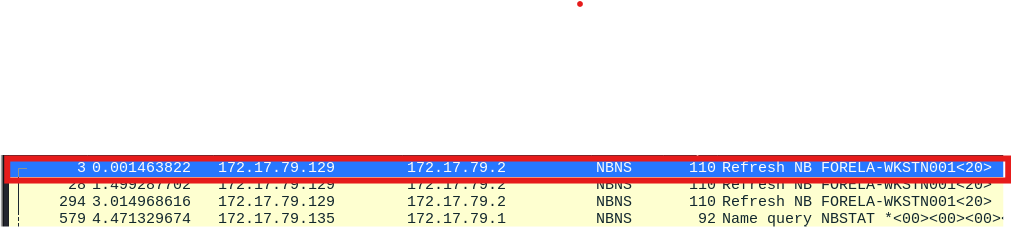
What is the IP Address for Forela-Wkstn002?
We used the same method as above to filter for Forela-Wkstn002.
Answer: (Repeat the same steps as for Forela-Wkstn001)

Which user account’s hash was stolen by the attacker?
We identified which user account’s hash was stolen by filtering for the
ntlmsspprotocol in Wireshark. This protocol is used in NTLM authentication, and by examining the traffic, we identified the account that was targeted by the attacker.Answer:
arthur kyle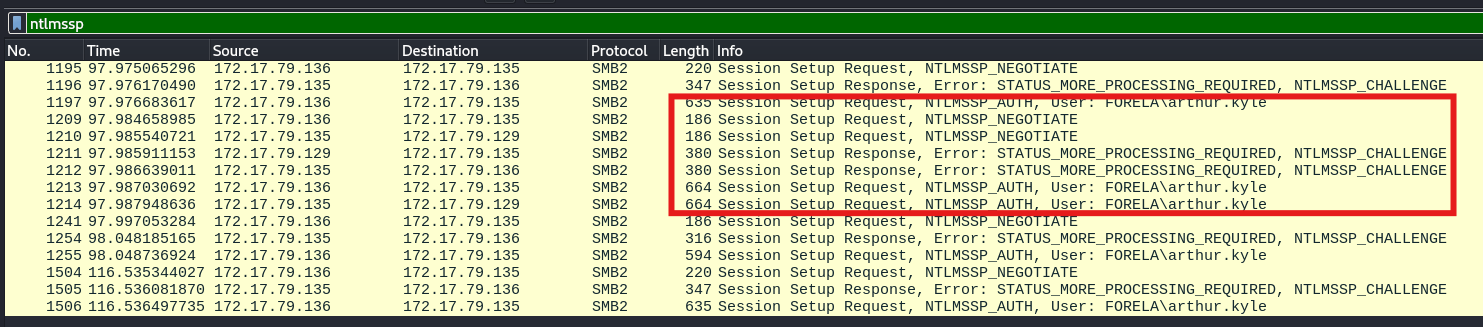
What is the IP Address of the Unknown Device used by the attacker to intercept credentials?
We identified the IP address of the unknown device used by the attacker to intercept credentials by using several methods. First, we filtered for the NBNS protocol in Wireshark and found a device with no hostname, which matched the attacker’s device. Additionally, we looked for an IP address involved in the authentication flow for the victim user that did not belong to any known workstation. We also analyzed anomalous logon events to pinpoint the source IP address.
Answer:
172.17.79.135
What was the fileshare navigated by the victim user account?
We identified the fileshare that the victim user account navigated to by filtering for
smb2traffic in Wireshark. We specifically searched for the keyword “BAD_NETWORK_NAME” in the packet details, which led us to the relevant fileshare path.Answer:
\\DC01\Trip
What is the source port used to log on to the target workstation using the compromised account?
The source port (
40252) was identified by filtering event logs for Event ID 4624, and then examining entries where the Security ID isNULL, Logon Type is3, the Logon Process isNtlmSSP, and the Authentication Package isNTLM. The source port is found within the Network Information section of the event details.Answer:
40252
What is the Logon ID for the malicious session?
To find the Logon ID, we looked at the same event and identified the LOGON ID value. After removing the leading zero, we found:
Answer:
0x64A799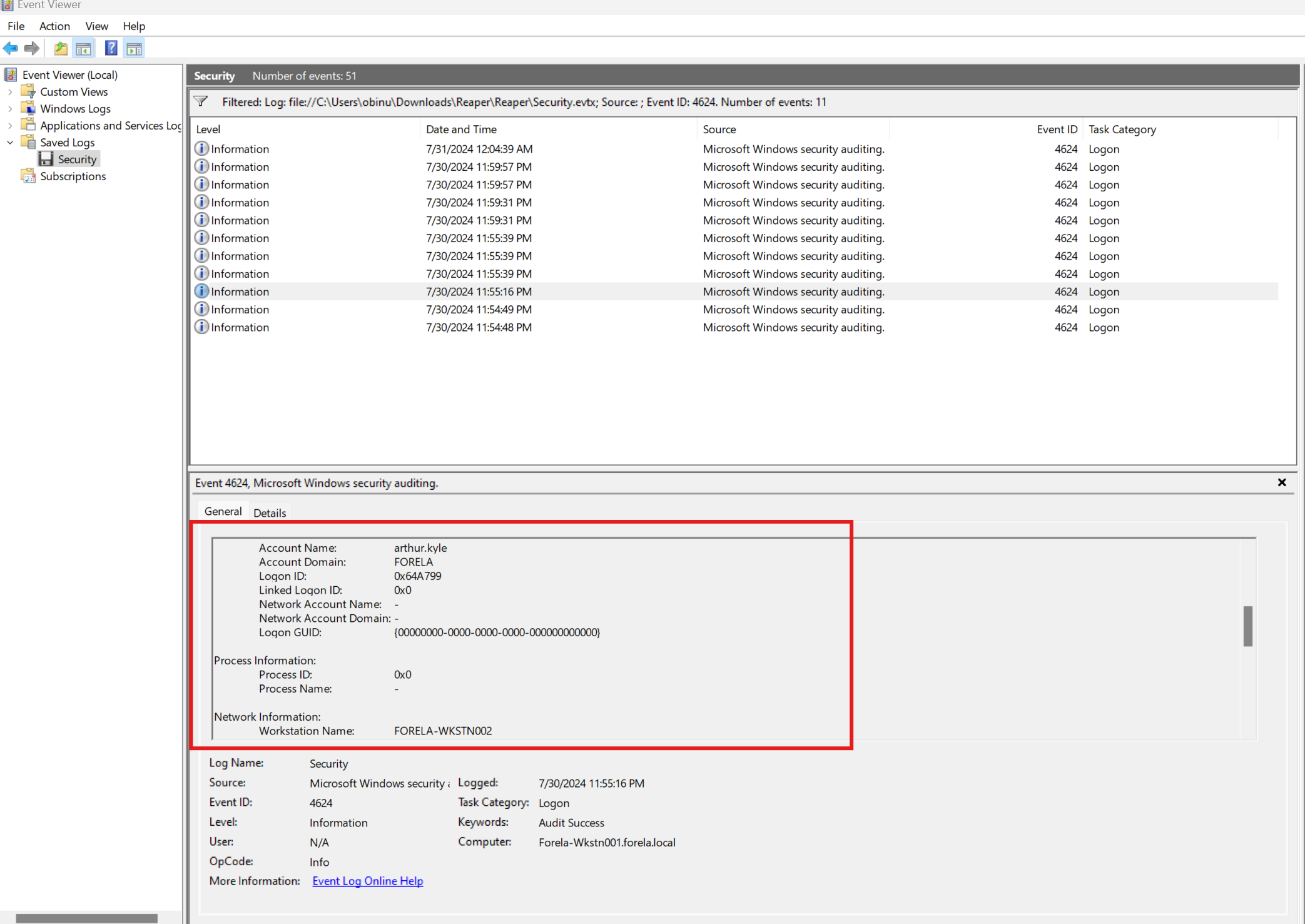
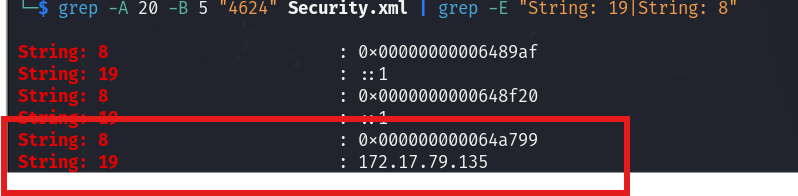
What is the workstation name and the source IP Address from which the malicious logon occurs?
We used the event we found for previous questions to answer the rest of them.
Answer:
FORELA-WKSTN002, 172.17.79.135
When did the malicious logon happen? Please make sure the timestamp is in UTC.
Answer:
2024-07-31 04:55:16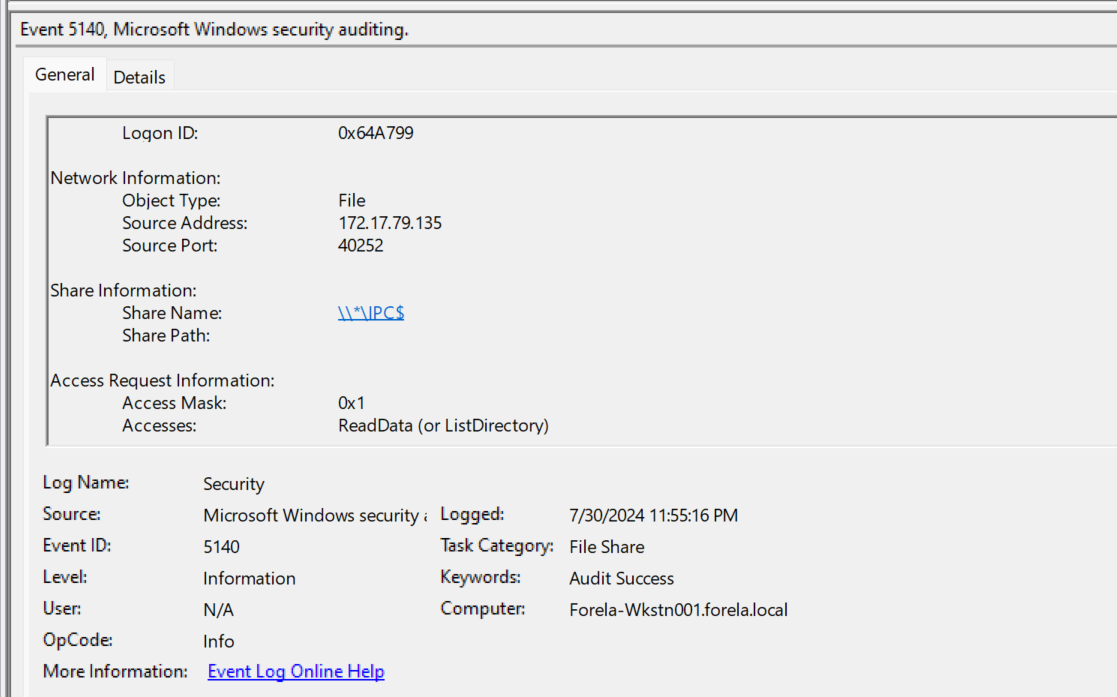
What is the share name accessed as part of the authentication process by the malicious tool used by the attacker?
Look for event ID 5140 and see the share name accessed. We can relate this event with the malicious session via the Logon ID we found before.
Answer:
\\*\IPC$